9 Key Technological Trends in Education for 2025

I get asked all the time what’s on the horizon for online learning. It feels like things are moving faster than ever, and it’s tough for course creators and instructional designers to keep up. One minute we’re talking about simple video courses, and the next, we’re diving into AI tutors and virtual reality field trips.
It’s a lot to take in, but it’s also incredibly exciting. The right technology makes learning more personal, more engaging, and more effective for our students. For creators like us, understanding these shifts is key to building courses and communities that truly stand out and deliver real results.
This guide is designed to cut through the noise. I’ve spent time digging into the biggest technological trends in education that are shaping how we will teach and learn in the coming years. We are going to explore what each trend means, how you can actually use it, and the impact it can have on your learners.
We will cover a lot of ground, from AI and machine learning to gamification, microlearning, and even blockchain. Think of this as your practical roadmap. I’m focusing on actionable insights to help you create amazing digital learning experiences and stay ahead of the curve. Let’s dive into what’s next.
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Education
Artificial intelligence is no longer just a concept from science fiction. It has firmly arrived as one of the most transformative technological trends in education today.
At its core, AI in education uses smart algorithms and machine learning to create more adaptive, efficient, and personalized learning journeys. These systems analyze vast amounts of student data, like quiz scores, time spent on tasks, and interaction patterns, to understand individual strengths and weaknesses.
This data-driven approach allows AI to tailor educational content in real time. Imagine a math platform that notices a student is struggling with fractions. It can automatically provide more practice problems, targeted video tutorials, or simpler foundational concepts until the student achieves mastery. This level of individual attention was once only possible with a one-on-one human tutor.
How It’s Being Used
We see AI making a real impact across the globe. For example, platforms like Carnegie Learning use sophisticated AI tutors to guide students through complex math problems, offering hints and feedback just like a human teacher would.
In the corporate training space, AI helps create adaptive learning paths for employees. This makes sure they learn the specific skills needed for their roles without wasting time on material they already know. Georgia State University even uses an AI-powered chatbot named ‘Pounce’ to answer thousands of questions from incoming freshmen, which has successfully reduced summer melt by over 21%.
Getting Started with AI
Integrating AI can feel daunting, but you can start small and scale up effectively.
- Start with a Pilot: Begin by implementing an AI tool in a single course or for a specific task, like automated grading for multiple-choice quizzes. This lets you test its effectiveness and gather feedback.
- Prioritize Data Privacy: Be transparent with learners about how their data is being used. Establish clear policies and ensure any third-party tools you use are compliant with privacy regulations.
- Blend AI with Human Touch: AI is most powerful when it supports human instructors. Use AI to handle repetitive administrative tasks or provide initial feedback, freeing up your time for more meaningful, in-depth interactions with learners.
The growth of AI in this sector is explosive, reflecting its immense potential to reshape how we teach and learn. The following infographic highlights the projected market growth and the rapid adoption of AI within learning platforms.
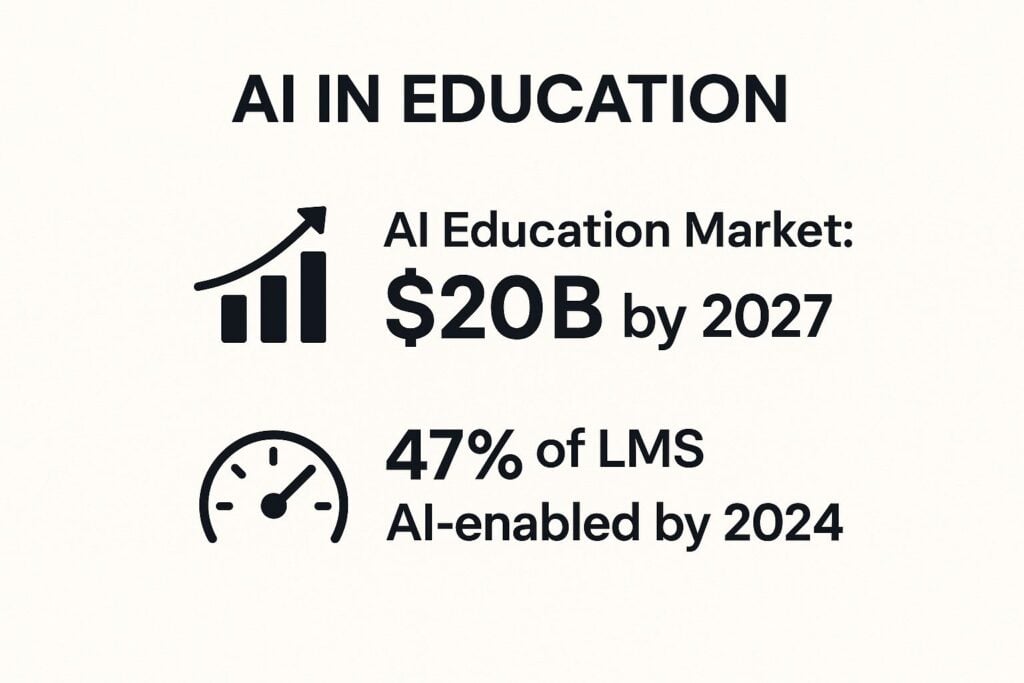
These numbers show a clear trend: AI is quickly becoming a standard feature, not just a futuristic add-on, in the educational technology landscape.
2. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Virtual and augmented reality are transforming learning from a passive activity into an active, immersive experience. These technologies are among the most exciting technological trends in education because they allow learners to step inside their subjects.
VR creates fully simulated digital environments, perfect for exploring a historical site or conducting a complex science experiment. AR, on the other hand, overlays digital information onto the real world, bringing diagrams and models to life right on a classroom desk.

This hands-on approach makes abstract concepts tangible and memorable. Instead of just reading about the human heart, a student can use VR to journey through its chambers. Instead of looking at a 2D picture of a dinosaur, they can use an AR app to see a T-Rex walking around their room. This deepens understanding and sparks a level of curiosity that traditional methods often struggle to achieve.
How It’s Being Used
Immersive learning is already making waves. Platforms like Labster provide over 2 million students with access to virtual science labs. There they can perform experiments that would be too dangerous or expensive for a physical classroom. In K-12, zSpace laptops are used in over 1,000 schools to deliver interactive STEM content in 3D.
Stanford University’s Virtual Human Interaction Lab uses VR for groundbreaking behavioral research, while ClassVR has deployed headsets across UK schools to create immersive lessons on everything from ancient history to outer space.

Getting Started with VR and AR
Diving into immersive technology is more accessible than you might think. Here’s how you can begin integrating it into your educational programs.
- Start with Mobile AR: You don’t need expensive headsets to start. Many powerful AR apps work on standard smartphones and tablets, offering a low-cost entry point. For specific insights into the future of AR in learning, consider exploring the top 8 augmented reality education examples for 2025.
- Keep Sessions Short: To prevent fatigue or sensory overload, begin with short, focused VR or AR sessions of about 10 to 15 minutes.
- Align with Learning Goals: Make sure every immersive experience is tied directly to a specific curriculum objective. The technology should enhance the lesson, not just be a novelty.
- Plan a Debrief: After an experience, hold a discussion. Ask learners what they observed, what surprised them, and how it connects to what they’ve been studying. This helps solidify the learning.
3. Gamification and Game-Based Learning
Gamification turns the learning process into an experience that is more engaging and motivating by borrowing elements from games. This powerful technological trend in education integrates mechanics like points, badges, and leaderboards directly into the curriculum.
It taps into our natural desire for achievement, competition, and reward. This transforms otherwise standard tasks into compelling challenges. The goal is to boost participation and help learners build lasting knowledge through active involvement.
Game-based learning takes this a step further by using actual games to teach specific concepts and skills. It places learners in an interactive environment where they must solve problems, think critically, and collaborate to progress. For a deeper dive into how this trend transforms learning, consider exploring What Is Gamification in Education and how it applies these engaging elements.

How It’s Being Used
The application of gamification is incredibly widespread and effective. Platforms like Kahoot! have seen over 9 billion participants engage in live, quiz-based games that make reviewing information fun and competitive.
In mathematics, Prodigy Math Game is used by over 50 million students, wrapping math curriculum into a fantasy role-playing game. Even language learning has been gamified by apps like Duolingo, which uses streaks, points, and friendly competition to keep its 500 million users motivated. These examples prove that when learning feels like playing, engagement and retention can skyrocket. You can explore more strategies for implementing these ideas with our guide on gamification for elearning.
Getting Started with Gamification
Bringing game mechanics into your learning environment is more accessible than you might think. Here’s how you can get started.
- Align Mechanics with Goals: Make sure every game element, whether it’s a badge or a leaderboard, directly supports a specific learning objective. The fun should always serve an educational purpose.
- Balance Competition and Collaboration: While leaderboards can motivate some, they may discourage others. Include collaborative challenges where learners must work together to succeed. This caters to different motivational styles.
- Offer Multiple Paths to Success: Design your gamified system to accommodate diverse learners. Allow individuals to achieve “wins” through different activities, such as exploration, completing extra challenges, or helping peers.
4. Learning Analytics and Big Data
Learning analytics and big data represent a monumental shift in understanding how learning actually happens. This powerful technological trend in education involves gathering, analyzing, and reporting on the vast digital footprints learners leave behind. The goal is to gain deep insights that can be used to improve course design, support struggling students, and ultimately optimize the entire educational environment.
Every click, quiz attempt, video view, and forum post creates a data point. When aggregated, this “big data” reveals patterns that were previously invisible. We can see which resources are most effective, identify students who are at risk of falling behind before they fail, and understand the specific learning paths that lead to success. This moves education from a one-size-fits-all model to one that is data-informed and highly responsive to learner needs.
How It’s Being Used
The application of learning analytics is already yielding impressive results. For instance, Purdue University’s “Signals” system analyzes student engagement data to provide early-warning alerts to both students and advisors. This has helped to significantly improve retention rates.
Similarly, Arizona State University uses its eAdvisor platform to guide students toward majors that fit their strengths and track their progress, boosting graduation outcomes. Platforms like Civitas Learning work with hundreds of institutions to build predictive models that identify at-risk students and guide intervention strategies.
Getting Started with Learning Analytics
Diving into data can seem complex, but a strategic approach makes it manageable and highly impactful.
- Establish Clear Data Governance: Before you collect anything, define what data you will gather, why you need it, and how you will protect it. Transparency is key to building trust with learners.
- Train Educators in Data Literacy: The data is only as good as the people interpreting it. Provide training for instructors and staff on how to understand the analytics and translate them into actionable teaching strategies.
- Combine Quantitative with Qualitative: Numbers tell part of the story, but not all of it. Supplement engagement metrics with qualitative feedback from surveys, interviews, and direct conversations to get a complete picture of the learner experience.
- Use Analytics to Support Judgment: Data should empower educators, not replace their professional judgment. Use analytics as a powerful tool to inform decisions, start conversations, and guide interventions, always keeping the individual student at the center.
5. Microlearning and Mobile Learning (m-Learning)
The days of hour-long lectures being the only option are fading. One of the most practical technological trends in education is the rise of microlearning and its perfect partner, mobile learning (m-learning).
This approach breaks down complex topics into small, digestible pieces of content, often just 3 to 10 minutes long. The goal is to deliver focused, bite-sized information that learners can absorb quickly and easily, fitting education into the natural gaps of their day.
This model is designed for how our brains actually learn and remember things. By concentrating on a single learning objective per lesson, microlearning improves retention and prevents cognitive overload. When paired with mobile devices, it becomes m-learning, giving people the power to learn anytime and anywhere. Whether on a morning commute or during a coffee break, learners can access short videos, interactive quizzes, or quick articles right from their smartphones.
How It’s Being Used
This trend is everywhere because it works. Language-learning app Duolingo built its entire model on 5-minute lessons, making it easy for millions to build a daily learning habit.
In the professional world, platforms like LinkedIn Learning offer thousands of short video modules that allow employees to quickly upskill in a specific area without dedicating hours to a full course. We also see it with Khan Academy, whose mobile app provides bite-sized lessons in math and science, making complex subjects accessible on the go for students of all ages.
Getting Started with Microlearning
Adopting a microlearning strategy is highly achievable and can have a massive impact on engagement.
- Design for Mobile First: Assume your learners will be on their phones. This means using large fonts, simple navigation, and vertical video formats. The experience must be seamless and distraction-free.
- Create Learning Pathways: While individual lessons are short, they shouldn’t be disconnected. Organize them into a logical sequence or pathway that guides learners through a broader topic step by step.
- Use Spaced Repetition: Boost long-term memory by reintroducing key concepts at increasing intervals. Send push notifications with quick quizzes or flashcards to reinforce what learners have already covered. You can discover various microlearning platforms that have these features built-in.
- Include Quick Assessments: End each micro-lesson with a brief, low-stakes quiz or interactive challenge. This provides immediate feedback and helps solidify the new information.
6. Blockchain Technology for Education

While often associated with cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology is emerging as a powerful and secure trend in education. At its core, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that creates tamper-proof digital records.
In an educational context, this means we can create secure and verifiable academic credentials. These can range from diplomas and certificates to individual course credits and skills badges.
This technology shifts ownership of academic records from the institution to the learner. Imagine a lifelong digital portfolio that you control, containing all your achievements from every institution you’ve ever attended. This makes it simple to share verified credentials with employers or other schools, eliminating the need for lengthy verification processes and protecting against fraudulent claims.
How It’s Being Used
Institutions are already pioneering this technology to enhance credentialing. For instance, MIT developed an open standard called Blockcerts. This allows them to issue digital diplomas that are secure, tamper-proof, and easily verifiable by anyone.
Similarly, the University of Nicosia in Cyprus was one of the first universities to issue academic certificates on the blockchain, giving their graduates full control over their own records. Companies like Learning Machine (now part of Hyland) have partnered with numerous universities to create blockchain-based digital transcripts and portfolios for students.
Getting Started with Blockchain
Adopting blockchain might seem complex, but you can approach it strategically.
- Launch a Pilot Program: Start by issuing a specific type of credential, like a professional development certificate or a digital badge for a workshop, on the blockchain. This allows you to test the process on a smaller scale.
- Collaborate on Standards: Work with other institutions or join consortia to help establish common standards. Interoperability is key for learners to build a comprehensive portfolio across different schools.
- Focus on User Experience: The underlying technology is complex, but the interface for students and verifiers should be simple and intuitive. Make sure users can easily access, manage, and share their credentials without needing to understand the technical details of blockchain.
7. Adaptive Learning Systems
Adaptive learning systems represent a major leap forward from the one-size-fits-all model of education. As one of the most impactful technological trends in education, these platforms use sophisticated algorithms to create a truly personalized learning journey for every single student.
By continuously analyzing data like a student’s answers, pace, and interaction patterns, the system adjusts the difficulty and type of content presented in real time.
This dynamic approach ensures that learners are always working within their optimal learning zone. If a student is acing a concept, the system can introduce more challenging material to keep them engaged. Conversely, if a student is struggling, the platform can automatically provide supplemental resources, simpler explanations, or foundational exercises to help them build mastery before moving on. This creates an incredibly efficient and effective educational experience tailored to individual needs.
How It’s Being Used
Adaptive learning is already transforming classrooms and corporate training programs. For instance, McGraw Hill’s ALEKS (Assessment and LEarning in Knowledge Spaces) platform is widely used in K-12 and higher education to create individualized learning paths in math and science. It pinpoints exactly what a student knows and doesn’t know, then charts a unique course to fill those knowledge gaps.
Similarly, platforms like Knewton Alta are used by universities to deliver courseware that adapts to each student, which helps improve grades and course completion rates.
Getting Started with Adaptive Learning
Integrating an adaptive system can significantly boost learner outcomes, and getting started is more accessible than ever.
- Ensure Robust Content: Your system is only as good as its content library. Make sure you have a wide range of materials covering various difficulty levels, from remedial to advanced, to support every possible learning path.
- Blend Tech with Teacher Support: Adaptive technology should empower educators, not replace them. Use the platform’s data to identify which students need extra one-on-one attention, allowing you to provide targeted, high-impact support.
- Monitor for Stagnation: Keep an eye on student progression data. If a learner seems stuck in a loop on a particular topic, it may be a sign that they need a different type of intervention that the system alone can’t provide.
8. Cloud Computing and Learning Management Systems (LMS)

The idea of a centralized digital classroom has become a reality, largely thanks to cloud computing. This technology powers modern Learning Management Systems (LMS), which are online hubs for course content, communication, and administration.
As one of the most foundational technological trends in education, a cloud-based LMS removes the need for schools and companies to host their own complex server infrastructure. Instead, everything is accessible online from any device with an internet connection.
This “anytime, anywhere” access is the cornerstone of modern hybrid and remote learning. An LMS allows instructors to upload materials, create assignments, grade submissions, and communicate with learners all in one place. For students, it provides a single, organized portal for their entire educational experience. They can access lecture notes, participate in discussion forums, and track their progress. It streamlines the entire learning workflow for everyone involved.
How It’s Being Used
Cloud-based LMS platforms are now standard in education and corporate training. Canvas LMS, for instance, is used by over 6,000 institutions to create engaging learning environments. In the K-12 and higher education space, Google Classroom has a massive footprint with 150 million users, offering a simple and integrated solution.
The open-source platform Moodle supports a global community of over 300 million learners. This demonstrates the flexibility and scale that cloud technology enables. These systems prove that a powerful LMS can be the digital backbone of any learning institution.
Getting Started with an LMS
Adopting an LMS is a big step, but a strategic approach makes it manageable and successful.
- Prioritize User Experience: Select a platform that is intuitive and easy to navigate for both instructors and learners. A confusing interface can create a major barrier to adoption.
- Plan for Integration: Choose an LMS that easily connects with other tools you already use, such as your student information system, video conferencing software, or content creation apps.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Don’t just launch the system, train your users. Offer workshops, create guides, and provide ongoing support to make sure everyone feels confident using the new platform. You can find several powerful LMS examples on learnstream.io to see what might fit your needs.
9. Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Classrooms
The Internet of Things, or IoT, is transforming the physical classroom into a smart, interconnected ecosystem. This trend moves beyond simply having devices in a room. It connects those devices to the internet and each other.
IoT in education uses sensors, smartboards, automated lighting, and even student ID cards to gather data and automate tasks. This creates a more responsive and efficient learning environment.
This network of devices can streamline classroom management and enhance the learning experience. For instance, an IoT system can automatically take attendance as students enter the room with smart ID cards. It can also adjust the lighting and temperature based on the time of day or occupancy, creating an optimal setting for focus. The data collected from these interactions helps educators understand how physical space impacts student engagement and learning outcomes.
How It’s Being Used
IoT is already making classrooms smarter around the world. Cisco’s Connected Classroom solutions, for example, help schools integrate various devices to facilitate remote learning and interactive lessons.
Georgia Tech has developed a “smart campus” with over 1,200 IoT devices that monitor everything from building occupancy to energy usage. This provides valuable data for operational efficiency. Similarly, Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative extends into schools, using IoT to create secure, automated, and interactive educational environments.
Getting Started with IoT
Deploying IoT in a classroom can seem complex, but a phased approach makes it manageable.
- Start with One Classroom: Begin with a pilot project in a single room to test the technology and its impact. This allows you to identify challenges and refine your strategy before a wider rollout.
- Prioritize Cybersecurity: Connected devices can be vulnerable. Implement strong security measures from the start, including secure networks and data encryption, to protect student and institutional data.
- Develop Clear Data Policies: Be transparent about what data you are collecting and why. Create clear privacy policies and make sure all stakeholders, including students and parents, understand them. This builds trust and ensures compliance.
Putting These Trends Into Action
Whew, that was a deep dive into the most exciting technological trends in education! We’ve covered a lot of ground, from the personalized pathways carved out by AI and adaptive learning systems to the immersive worlds built with VR and AR. We explored how gamification can inject fun and motivation into lessons, and how microlearning makes education fit into our busy lives.
Seeing all these innovations laid out can feel a bit overwhelming. It might seem like you need to become a tech wizard overnight to keep up. But that’s not the real takeaway here. You don’t need to implement every single trend tomorrow.
The core message connecting all these tools, from learning analytics to blockchain, is a fundamental shift in how we approach learning. The future of education is more personalized, flexible, engaging, and data-informed than ever before. It’s all about meeting learners where they are, with the right content, in the right format, at the right time.
Your Actionable Next Steps
So, where do you go from here? Instead of trying to boil the ocean, I recommend a more focused approach. Let’s make this manageable and impactful.
Step 1: Reflect and Prioritize. Look back at the trends we discussed. Which one genuinely sparked your curiosity? Which one directly addresses a problem you’re currently facing with your learners? Maybe your completion rates are low, and gamification or microlearning could be the perfect solution. Or perhaps you’re struggling to teach a complex, hands-on concept, making VR a fantastic option to explore. Pick just one or two that align with your immediate goals.
Step 2: Start Small with a Pilot Project. You don’t need to overhaul your entire curriculum. Think small. For example, if you’re interested in AI, you could experiment with an AI-powered chatbot to answer common student questions for a single module. If gamification is your choice, try adding a simple leaderboard or a badge system to one of your existing courses. This low-stakes approach allows you to test the waters, gather feedback, and learn without a massive investment of time or money.
Step 3: Focus on Pedagogy, Not Just Technology. This is the most critical piece of advice I can give. The goal is always to improve the learning experience, not just to use tech for tech’s sake. Before you implement anything, ask yourself: “How will this specific tool actively help my students understand the material better, stay more engaged, or achieve their learning outcomes more effectively?” The technology should always serve your educational strategy.
The Bigger Picture: Building the Future of Learning
Mastering these concepts is about fundamentally enhancing your ability to create transformative learning experiences. By thoughtfully integrating these technological trends in education, you can build courses that are not only more effective but also more enjoyable and accessible for a wider audience.
You’re creating learning environments that respect the individual, empower them with data, and engage them in ways that traditional models simply can’t. This is how you build a loyal community and a successful digital education business that truly stands out.
The digital learning landscape will undoubtedly continue to evolve. New tools will emerge, and existing ones will become even more sophisticated. But by staying curious, focusing on what truly helps people learn, and taking small, deliberate steps forward, you’ll be perfectly positioned to not just adapt but to thrive. You’re not just an educator or a course creator, you are an architect of the future of learning.






